Both iPhone 12 Pro and iPad Pro 2020 have a new sensor that adds a deep scan of the scene for better photos called Lidar, But the future points to what is beyond that, and Apple is optimistic about this technology and relies on it a lot, which is a completely new technology limited to the iPhone 12 series, specifically the iPhone 12 Pro and iPhone 12 Pro Max. And sensor Lidar It is a black dot near the rear camera lens, about the same size as the flash, and it is a new type of depth sensor that can make a difference in many interesting ways. It is a term that you will start hearing a lot in the coming days, so let's get to know it more, and what is the purpose that made Apple develop? And where might technology go next?

what does it mean Lidar ؟
Flame Lidar An abbreviation for “Light Detection and Ranging” meaning the detection of light and the determination of the range “distance” by illuminating the target and scanning it with a laser beam, then returning it to the source again, then measuring this reflection and the times of return of those rays and wavelengths to create three-dimensional digital models of the target, and this is done In milliseconds.
The technique is used Lidar Commonly used for creating high-resolution maps, it is also used in archeology, geography, geology, earthquakes, forests, the atmosphere, altimeters, driverless car control, and more.
The history of the technology Lidar

The roots of this technology go back to the 1930's, when the basic concept of the Lidar It was limited to the use of powerful searchlights to explore the Earth and the atmosphere. Then it has since been used extensively in atmospheric and meteorological research.
But the beginning of the great development of this technology and its spread was in 1961, that is, shortly after the invention of the laser, as Hughes Aircraft Corporation at that time presented the first lidar-like system dedicated to tracking satellites, combining laser-focused imaging with the ability to calculate distances by measuring time Signal return using appropriate sensors and data acquisition electronics, it was originally called "Colidar" which is an acronym for "Coherent Light Detecting and Ranging", which is a derivative of the term "Radar".
However, LiDAR did not attain the popularity it deserved until twenty years later. It was only during the XNUMXs after the introduction of the Global Positioning System (GPS) that it became a popular method for calculating accurate geospatial measurements. Now, the scope of that technology has spread across many domains.
How does lidar work to sense depth?
Lidar is a type of camera Time-of-flightSome other smartphones measure depth with a single pulse of light, while the iPhone that uses this type of lidar technology sends waves of laser pulses into a network of infrared points, which are pulses of light invisible to the human eye, but you can see them with a camera For night vision, then the variable distances of an object in the scene are calculated. And these light pulses, along with the information collected by the system, generate accurate three-dimensional information of the target scene and object, then other elements such as the processor and the rest of the components come in turn to collect and analyze the data and produce the final result to work to the fullest extent.

LiDAR follows a simple principle, shedding laser light at an object and calculating the time it takes to return to the LiDAR sensor. Given the speed at which light travels “about 186000 miles per second,” the precise distance measurement process across LiDAR appears incredibly fast.
Isn't a lidar sensor the same as two sensors? Face ID ؟
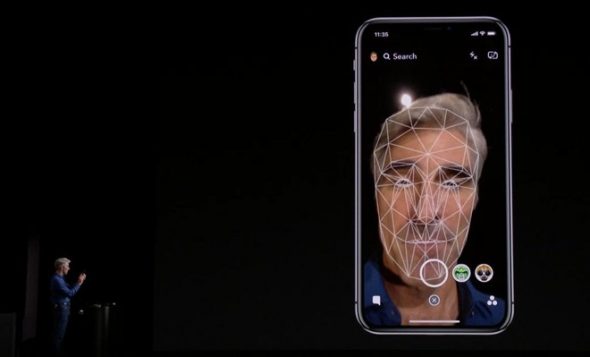
It is, but with a longer range. The idea is the same, as the TrueDepth camera in Face ID fires an array of infrared lasers, but has a short range and only works a few feet away. While the lidar sensors operate at a range of up to 5 meters!
A lidar sensor is already present in a lot of other technologies
LiDAR is a ubiquitous technology. They are used in self-driving or auxiliary cars. They are used in robots and drones. AR headsets like HoloLens 2 have a similar technology, defining room spaces before placing virtual XNUMXD objects in them. The lidar technique, as mentioned earlier, also has a very long history.

Microsoft's old Xbox depth-sensing accessory was Kinect, which was a camera with an infrared depth-sensor as well. Apple acquired Prime Sense, the company that helped create the Kinect technology, in 2013. Now, we have the TrueDepth technology that scans the face, and the LiDAR sensor in the rear camera array of the iPhone 12 Pro that detects depth even more.
The iPhone 12 Pro camera works better with the lidar sensor
Time-Of-Flight cameras on smartphones tend to be used to improve accuracy and focus speed, and the iPhone 12 Pro does the same, focusing better and faster on improving low-light, up to six times that of low-light conditions.
Better focus is a plus, as iPhone 12 Pro can add more image data thanks to XNUMXD scanning. Although this element has not yet been identified, the front TrueDepth camera that senses depth has been used in a similar way with applications, and third-party developers can dive into some ideas using these new technologies and this is what we will actually see.
It also benefits augmented reality tremendously
Lidar allows iPhone 12 Pro to launch AR apps more quickly, and create a quick scene map to add more details. Much of the augmented reality updates in iOS 14 make use of lidar to create virtual objects and hide them behind real objects, and it comes to placing virtual objects inside more complex room components with great precision.
Developers are using lidar to scan homes and spaces and perform scans that can be used not only in augmented reality, but to save place models in formats like CAD.
It was tested on an Apple Arcade game, Hot Lava, which actually uses lidar to clear the room and all its hindrances. And was able to place virtual objects on the stairs, and hide objects behind realistic objects in the room.

We expect more AR apps that will start adding Lidar support more professionally and go beyond what we mentioned.
Many companies dream of headphones that combine virtual objects with real things, as they will adopt augmented reality glasses, which Facebook, Qualcomm, Snapchat, Microsoft, Magic Leap, and most likely Apple and others are working on, will rely on the presence of advanced XNUMXD maps of the world and placing virtual objects on them.

These XNUMXD Maps are now created with special scanners and equipment, almost the same as the global vehicle scanning version of Google Maps. But there is the possibility that special devices may eventually help people gather this information or add additional data on the go.
Once again, AR headphones like Magic Leap and HoloLens pre-scan your environment before putting things in, and Apple's lidar-equipped AR technology works the same way. In this sense, the iPhone 12, 12 Pro and iPad Pro are similar to AR headphones without the headphone part. This, of course, could pave the way for Apple to eventually create its own glasses.
Apple isn't the first to discover technology like this on the phone

Google had the same idea when the Tango project was created, and it is mainly targeting augmented reality technologies, and the initial prototypes of the Tango project were smart mobile devices “phones and tablets” based on the Android system that have the property of spatial perception of the environment in which the device is located by tracking The three-dimensional movement and capturing the shape of the surrounding environment in real time, by adding an advanced vision system, image processing and specialized sensors, and was used only on two phones, including the Lenovo Phab 2 Pro.

The advanced camera suite also contains infrared sensors and can map rooms, create XNUMXD scans and deep augmented reality maps and measure indoor spaces. These Tango-equipped phones were short-lived, and were replaced by computer vision algorithms and artificial intelligence that sensed the estimated depth through cameras without the need to add real sensors, as happened in the Pixel phones from Google.
With this, the iPhone 12 Pro is the one who reformulated the Lidar technology, working to provide it better and bringing a technology that was established for a long time and extended to other necessary industries, and now it is being integrated into self-driving cars, AR headsets, and much more.
Sources:
geospatialworld | cnet | wikipedia



26 comment